If your car is making strange noises and you’re not sure why it might be time to take a look at the catalytic converter. This component is responsible for reducing harmful emissions from your vehicle, and if it’s not working properly, it can cause all sorts of problems. In this blog post, we will discuss the symptoms of a bad catalytic converter and the replacement cost. Keep reading to learn more!
What is a Catalytic Converter And How does it work?
A catalytic converter is a device that converts harmful exhaust gases from an internal combustion engine into less-harmful substances. It works by using a combination of precious metals, including platinum and palladium, to break down the pollutants into harmless molecules such as oxygen and water vapor. The catalyst inside the converter helps speed up the process by lowering the amount of energy needed for the reaction to occur. The converter also helps reduce engine noise and reduces emissions of unburned hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen oxides.

The catalytic converter is located in the exhaust system of a vehicle and works by converting harmful exhaust gases into less harmful substances before they are released into the atmosphere. The main component in a catalytic converter is a ceramic monolith, which is made up of an array of tiny channels that are coated with precious metal catalyst materials such as platinum, palladium, and rhodium. These metals act as a catalyst, meaning they speed up the chemical reaction that breaks down pollutants into harmless molecules. The ceramic monolith also helps to trap and reduce emissions of hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen oxides.
Where is a catalytic converter is located?
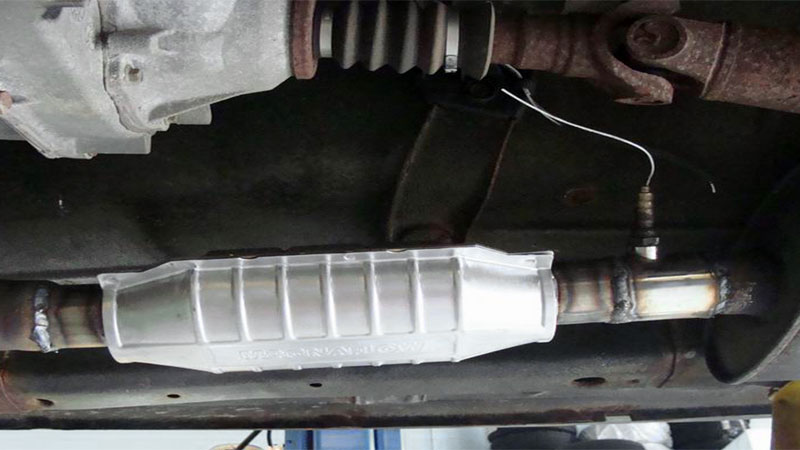

Located underneath your vehicle’s undercarriage, the catalytic converters are connected in series with other essential exhaust system components. Inline engines feature a lone converter while V-configuration ones generally include two (one for each bank). Catalytic converters are usually easily recognizable due to their unmistakable rectangular or oblong metal design. In most cases, your car’s catalytic converter will have two different openings; the first for bringing in exhaust from the engine, and another for releasing it out of the tailpipe.
Clogged vs Bad Catalytic Converter
People tend to group together “clogged” and “bad” when talking about catalytic converters, however, these phrases don’t always mean the same thing.
A clogged catalytic converter is a type of vehicle emission-control device that has become plugged up due to the accumulation of contaminants. Commonly, these contaminants are created as by-products of chemical reactions in the exhaust system itself, but they can also come from outside sources like engine oil, dirty fuel, and road salt. When a catalyst becomes clogged, it can no longer properly filter out pollutants from exhaust fumes and may even cause higher levels of emissions than usual. As such, it’s important to have your catalytic converter inspected regularly to make sure it isn’t blocked or restricted.
On the other hand, a bad catalytic converter is one that has been damaged or worn down over time and is no longer able to complete its job efficiently. This could be due to external factors like physical damage, internal degradation caused by extreme temperatures, or long periods of vehicle idling. In either case, the result is poor performance when it comes to reducing tailpipe emissions.
What Causes a Catalytic Converter to Go Bad?
A catalytic converter is an essential part of your vehicle’s exhaust system. It helps to reduce pollutants in the exhaust, making it less harmful to the environment. Unfortunately, over time a catalytic converter can fail due to a variety of reasons. The most common causes of catalyst failure include:
Faulty Spark Plugs

A faulty spark plug means less efficient combustion and increased exhaust emissions. This can cause the catalytic converter to overheat, which often results in reduced efficiency or failure.
Built-Up Carbon Deposits
Over time, exhaust residue and carbon deposits can accumulate in the catalyst restricting airflow. This restricts oxygen from entering the system, which causes the catalytic converter to become blocked and less effective at removing pollutants.
Oil or Coolant Leaks
Leaks in the engine oil or coolant system can contaminate the catalytic converter, causing it to become clogged and ineffective. It is important to regularly check your vehicle for any such leaks and have them repaired as soon as possible.
Exhaust Gas Temperature
A high exhaust gas temperature can cause the catalyst to overheat and become damaged. This is usually caused by an engine misfire or incorrect ignition timing, which can both lead to increased emissions and reduced efficiency.
Fuel Quality
Low-quality fuel can contain high amounts of sulfur, which can corrode the catalytic converter’s internal components. This reduces its ability to convert pollutants, leading to increased emissions and engine performance problems.
Excessive Oil Consumption
If your vehicle is burning oil excessively, it will be released into the catalytic converter and coat the walls. This reduces its ability to convert pollutants and leads to a rapid decrease in efficiency and performance.
Age and Wear
Over time, catalytic converters become less efficient due to age and wear. As the metals in the catalyst become corroded, their ability to convert pollutants decreases. Regularly inspecting and replacing catalytic converters can help to keep your vehicle running correctly.
Overall, it is important to regularly maintain your vehicle and address any issues that could lead to a catalytic converter failure. This will help you avoid costly repairs and keep your car running smoothly.
What Are The Symptoms Of A Bad Catalytic Converter?
A bad catalytic converter can cause a variety of problems that can be difficult to diagnose. The most common symptoms of a faulty catalytic converter are:
Rotten Egg Smell From Exhaust

Do you smell something distressingly like rotten eggs? It’s an indication of a failed catalytic converter. Gasoline contains a little amount of sulfur which breaks into hydrogen sulfide through the combustion process, emitting an unmistakable stench.
When your catalytic converter is functioning properly, it converts the stinky sulfide into odorless sulfur dioxide. If your catalytic converter isn’t doing its job correctly though, then those noxious gases containing hydrogen sulfide will escape from your exhaust, leaving an unpleasant smell in their wake.
Loss of Power
Faulty catalytic converters can also cause a noticeable reduction in engine power. This is due to the fact that it restricts the flow of exhaust gases. Without a free-flowing system, your vehicle isn’t able to burn fuel as efficiently which then affects the overall performance of your engine. This is especially noticeable when accelerating, as the car will struggle to reach higher speeds and have difficulty climbing hills.
A Decrease in Fuel Economy

The decreased efficiency resulting from a bad catalytic converter can also lead to a decrease in fuel economy. Your engine may be running inefficiently, which means that your vehicle will have to burn more fuel in order to achieve the same performance. If you’re noticing a decrease in mileage, it could be an indication that your catalytic converter needs attention.
Increased Exhaust Emissions
Another common symptom of a faulty catalytic converter is an increase in exhaust emissions. This can be easily spotted if your vehicle has failed its emissions test, as this indicates that your catalytic converter is not doing its job properly. Additionally, foul odors coming from your exhaust pipe can also be a sign of a bad catalytic converter.
Backfiring or Misfiring Engine
If your catalytic converter is not functioning properly, it can cause the engine to misfire or backfire. This is usually caused by an insufficient amount of oxygen being present in the exhaust system due to a lack of catalytic activity. If you notice any trouble with your vehicle’s engine, it would be wise to check the catalytic converter as soon as possible.

An Illuminated Check Engine Light
A common symptom of a bad catalytic converter is an illuminated check engine light on your dashboard. The oxygen sensors in modern vehicles can measure the efficiency of catalytic converters by inspecting exhaust gas levels.
If these sensors identify that the exhaust gases are not being properly catalyzed, a “Check Engine Light” will be activated. This is an indication to drivers that something isn’t right although it doesn’t precisely specify what the issue may be as this light can signify various problems.

Exhaust smoke coming out of your car’s tailpipe is dark
If the catalytic converter has gone bad, then the exhaust smoke coming from your car’s tailpipe will be darker than usual. The lack of catalytic activity will lead to incomplete combustion of fuel, leading to an excessive amount of carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons being released through the exhaust system.
When these gases are not properly catalyzed, they will appear as dark smoke. If you notice unusually dark exhaust fumes coming from your car, then it would be wise to investigate the catalytic converter further.
Engine Stalling or Hesitation
If your engine stalls or hesitates when accelerating, it could be a sign that the catalytic converter is malfunctioning. The converter might be clogged or partially blocked, preventing the proper amount of oxygen from reaching the engine. This can cause hesitation or stalling when you try to accelerate, as there is not enough of an exhaust flow to power the engine.
Failed Emissions Test
Most parts of the United States require vehicles to pass an emissions test in order for them to be legally driven on the road. If your vehicle has failed its emissions test, then it could be a sign that your catalytic converter needs attention. The inability of the catalyst to efficiently convert toxic gases into non-toxic gases is causing too much pollution and will need to be repaired or replaced in order to pass the test.
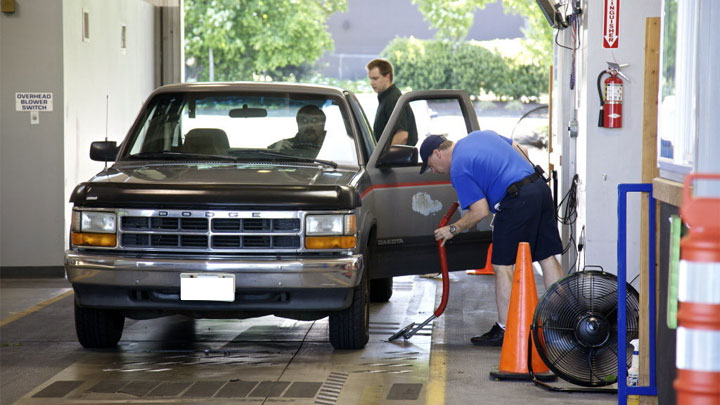

Depending on your vehicle’s model and year of manufacture, car diagnostics can be conducted either with the OBD2 port (for cars made after 1996) or through a hose connected to the tailpipe, gauging levels of toxic gases released from vehicles manufactured before 1996.
Rattling Noise From The Exhaust
Lastly, a bad catalytic converter can cause a rattling noise from the exhaust system due to the buildup of unburned fuel. This is usually caused by an insufficient amount of oxygen in the exhaust system, which can lead to a buildup of fuel particles and debris. This can lead to blockages and damage within the catalyst and eventually cause a rattling noise when the vehicle is in motion.
Holes in the Catalytic Converter
If you are able to see holes or cracks in the catalytic converter, then it is likely that you have a bad catalytic converter. This is usually caused by corrosion of the internal components due to overheating or the buildup of debris. If your catalytic converter has visible signs of damage, then it will need to be replaced as soon as possible.
In conclusion, if you are experiencing any of these symptoms with your car, it may be time to check your catalytic converter and have it inspected by a professional. Additionally, regular maintenance of your exhaust system can help prevent issues from arising and keep your catalytic converter functioning optimally.
Can a Bad Catalytic Converter Be Fixed?
No, a bad catalytic converter must be replaced. Catalytic converters are used to reduce harmful exhaust emissions from vehicles. When the catalytic converter fails, it can no longer do its job efficiently and must be replaced. However, minor structural issues can be repaired to a satisfactory degree, but they may still entail some expenses.
The life span of a catalytic converter depends on the quality of fuel used in the vehicle and how well-maintained it is. A clogged or bad catalytic converter will reduce engine performance and increase emissions, so it’s important to replace it as soon as possible.
When replacing a catalytic converter, you should always use an OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) part that is specifically designed for your make and model of vehicle. You can find these parts at most auto parts stores or online retailers.
Is it necessary to replace a bad catalytic converter?
Yes, it is necessary to replace a bad catalytic converter when it has gone beyond its peak efficiency. Over time, these converters become clogged due to lack of maintenance or as a result of using poor-quality fuel which eventually reduces their effectiveness and efficiency.
It is important to note that a bad catalytic converter will eventually cause engine misfiring, reduced fuel economy, and higher emissions. If left untreated, it can even lead to complete engine failure as the prolonged buildup of toxic pollutants will begin corroding other components in the vehicle’s exhaust system. Additionally, if your car fails an emissions test due to a faulty catalytic converter, it may not be allowed on the road until repairs are made.
Replacing a bad catalytic converter is therefore essential for the health of your vehicle and for the environment. A mechanic will usually inspect the exhaust system to identify any problems and then recommend a new catalytic converter if needed.
How much does it cost to replace a catalytic converter?
Replacing a catalytic converter can be costly due to its components being made up of precious metals such as platinum and palladium, but the exact cost will depend on several factors. The year, make, and model of your vehicle will affect parts costs, as well as any additional labor that might be required to complete the job. Additionally, the type of catalytic converter you choose to replace your existing one will also influence the total cost of the repair.

Gasoline Engines – 1981 and Newer
Since 1981, nearly all gasoline engine cars feature a three-way catalytic converter. Compared to the simpler designs of older vehicles, this design is more complex and as a result, parts cost significantly higher. Replacement of a catalytic converter in newer cars will typically cost between $500 and $2,200. Components alone can range from $400 to $2,000 while labor is estimated at one hour and between $75 to$150. All-in-all this investment may save you on future repairs as well as provide peace of mind for your safety.
Gasoline Engines – Before 1981 (and Diesel Engines)
Due to their simple design, two-way catalytic converters for gasoline engine cars made before 1981 and most diesel engines (regardless of age) are relatively inexpensive to replace. Replacing a catalytic converter in an older car will typically total around $175 to $750. You’ll pay approximately $100-600 for the parts and another $75 – 150 in labor fees. Also, be aware that if your vehicle is either old or rare, replacing its cat can become costly due to rarity.
Now that you know what factors will affect the cost of replacing a catalytic converter and how much it could cost for different vehicles, you can make an informed decision about your repair. Although replacing a catalytic converter is not cheap, it’s important to factor in its long-term value: It helps reduce emissions and keeps your vehicle running efficiently.
Is It Worth Replacing Your Catalytic Converter?
When a catalytic converter becomes clogged or otherwise malfunctions, it can cause your car to run inefficiently and reduce its performance. To maintain the efficiency of your vehicle, you may need to replace your catalytic converter. But is it worth it?
The cost of replacing a faulty catalytic converter can range from $300 to $2,000 or more depending on the make and model of your vehicle. However, this cost may be worth it in the long run as a faulty catalytic converter can result in decreased fuel efficiency, increased emissions from your car, and other problems related to engine performance.
When considering whether replacing a catalytic converter is worth it, you should weigh the cost of repair against the long-term benefits. A well-functioning catalytic converter helps to reduce tailpipe emissions and make your car more fuel efficient. Additionally, it helps to ensure that your vehicle runs properly and keeps you safe on the road.
Do You Have To Break In A New Catalytic Converter?
To ensure that your newly installed catalytic converter has a long, trouble-free life, it is important to follow the break-in procedure. Ask your mechanic if this process will be taken care of as part of the installation or make sure you do it yourself in order to guarantee maximum performance from your vehicle.
The break-in process is not complicated and can generally be completed in a few simple steps:
Step 1
First, ensure that the new catalytic converter is firmly bolted to the vehicle’s exhaust system. To make sure nothing has gone wrong during installation, check for any leaks or rattling noises from the exhaust pipe.
Step 2
Once it is confirmed that the catalytic converter has been securely installed, start your engine and let it idle for a few minutes. This allows the new catalyst to warm up gradually and evenly. After it has had time to warm up, accelerate at a moderate speed paying attention to any irregularities in performance such as misfires or hesitation while shifting gears.
Step 3
Once you have reached a steady speed, let the vehicle idle again for around 10 minutes and then switch off the engine. This will give the catalytic converter time to cool down evenly and help it ‘settle’ into its new home. The break-in process is now completed and your vehicle is ready to hit the roads.
In conclusion, it is recommended to break in a new catalytic converter after installation. This simple process helps the new catalyst settle into place and ensures that it performs at its optimum level. Make sure you follow your mechanic’s instructions or take the time to do it yourself in order to get maximum performance from your vehicle.
What Is The Average Lifespan Of A Catalytic Converter?
With proper maintenance and care, the catalytic converter can remain in good condition for up to 150,000 miles before needing a replacement. However, this can vary depending on a number of factors. Factors that can affect the lifespan of a catalytic converter include:
- Driving habits: If you drive aggressively or have bad driving habits, it can cause undue stress on the converter and shorten its lifespan.
- Vehicle age: Some older vehicles may not have had the most reliable parts used in the construction of their catalytic converters and may not last as long.
- Quality of fuel: Using poor quality or contaminated fuel can damage the converter, causing it to fail prematurely.
- Maintenance and care: Regular maintenance on your vehicle can keep it running in top condition, including the catalytic converter. This will help extend its life.
- Environmental conditions: Living in an area with high levels of air pollution or extreme temperatures can cause the catalytic converter to wear out faster than normal.
In general, with proper care and maintenance, a catalytic converter should last up to 150,000 miles before needing replacement. However, it is important to note that the lifespan of a catalytic converter can vary depending on the above factors. If you are unsure, it is always best to consult your vehicle’s manufacturer or a qualified mechanic for advice. This way, you can ensure that your catalytic converter is functioning correctly and getting the most out of its life.
Can a Clogged Catalytic Converter Be Cleaned?
The answer to this question is yes, a clogged catalytic converter can be cleaned. However, the most effective way to do this depends on the type and severity of the clog present. Generally speaking, minor blockages can be cleared of deposits with an external cleaning solution and some internal maintenance work in order to restore the proper functioning of the part. In more extreme cases, it may be necessary to replace the entire catalytic converter.
When looking for external cleaning solutions, there are a few methods available. You can try using an aerosol spray that is designed specifically for this purpose. This type of cleaner contains specialized chemicals which will dissolve any deposits present in the exhaust system and help clear the clog. Alternatively, you can opt for an engine decarbonizing treatment. This is a more intensive cleaning process that involves removing deposits from the combustion chamber and valves in order to improve the engine’s performance overall.
In terms of internal maintenance work, one of the most common methods used to clean clogged catalytic converters is to use a specific-use mechanical brush. This tool is designed to dislodge any deposits inside the converter, allowing them to be more readily removed. This process can also help reduce the backpressure in the exhaust system, helping improve fuel economy and overall engine performance.
Finally, if all other methods have failed or are not an option due to the severity of the clog, replacing the catalytic converter may be necessary. This is a more involved and expensive project, but it is often the only way to guarantee that the converter works properly. It is important to note, however, that this should only be done as a last resort.
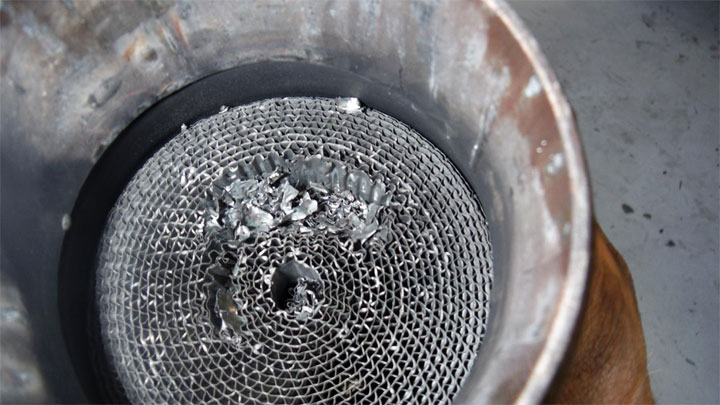

How to Help Prevent Clogging In Catalytic Converters?
One of the main causes of catalytic converter clogging is the build-up of particulate matter (PM) such as soot, ash, and other contaminants. These tiny particles accumulate inside the converter over time, blocking the flow of exhaust gases and reducing its efficiency. To help prevent this from happening, there are a few steps you can take:
- Regularly inspect the condition of your converter and replace it when necessary. You can usually find this information in your car’s owner’s manual.
- Make sure your engine is running properly by having regular tune-ups and oil changes, as well as replacing spark plugs, air filters, and fuel filters as needed.
- Use only high-quality fuel and engine oil that is designed for use in your car’s make and model, as specified by the manufacturer.
- Do not try to modify or tamper with the catalytic converter in any way, as this can damage it permanently.
- If your vehicle has a diesel engine, make sure to use the appropriate fuel and lubricants. Diesel fuel can contain higher levels of sulfur than normal gasoline, which can lead to soot buildup in the converter.
- Make sure you are not “over-revving” your car or running it at high speeds for extended periods of time. This can produce more soot in the exhaust and clog the converter faster.
- Take your car to a certified automotive technician or dealership as soon as possible if you notice any changes in performance, smell, or sound coming from the exhaust system. Having these issues resolved quickly can help prevent long-term damage to the converter.
Following these simple steps should help keep your catalytic converter free of clogs and working optimally. If you ever have any questions or concerns about the condition of your vehicle’s exhaust system, be sure to get in touch with a certified technician as soon as possible. They will be able to diagnose and repair the issue quickly and effectively.
Wrapping Up
In conclusion, a catalytic converter is an important car emission control device. It helps remove harmful pollutants from exhaust gases before they are released into the atmosphere and it can cause a lot of problems if it’s not working properly. A bad catalytic converter will typically present itself with symptoms such as decreased acceleration, engine misfires, and an illuminated check engine light on the dashboard. If you suspect that your vehicle is having issues with this component, it’s important to get it checked out right away. In some cases, a failing catalytic converter can be repaired by cleaning or replacement of sensors – but often it needs to be completely replaced. The cost of replacing the catalytic converter varies depending on the make and model of your car, but it can range anywhere from a few hundred dollars up to several thousand dollars in some cases. Therefore, it is always best to get the problem looked at by a professional to ensure that you don’t face any unexpected repair costs down the road. Luckily, we have compiled all the information you need to know about cats so that you can make the best decision for your car.
Frequently Asked Questions
Replacing a catalytic converter is an essential part of maintaining your vehicle’s emissions performance and can be an expensive repair if not covered by the manufacturer. Fortunately, if your car is less than eight years old with fewer than 80,000 miles, it may still be under the Federal emissions warranty provided by the vehicle’s manufacturer. This means that you could be eligible for a free replacement catalytic converter. To confirm your eligibility, you should contact the service department of the local new-car dealer that carries the same brand as your vehicle.
Technically, yes, but doing so is highly inadvisable and can be dangerous. A catalytic converter serves an important function in reducing harmful emissions from a car’s exhaust fumes. By removing the catalytic converter, you may be exposing yourself to dangerous levels of toxic gases such as carbon monoxide or nitrogen oxide. Additionally, driving without a catalytic converter can also lead to other issues such as decreased fuel efficiency, increased noise pollution, and decreased engine performance. It is therefore highly recommended that you do not drive a car without a properly functioning catalytic converter.
Catalytic converters have become a major target for thieves, who are attracted by the precious metals contained in the device. These metals are valuable and can be sold for scrap value and can fetch up to $200 per converter. Cars with higher ground clearance, such as SUVs and trucks, are particularly vulnerable to catalytic converter theft because they are easier to access from underneath the vehicle.
The short answer is yes. Though a bad catalytic converter is no longer usable for its purpose, it usually still contains valuable metals that can be recycled or sold to scrap metal dealers. A typical catalytic converter contains platinum, palladium, and rhodium, which are worth quite a bit of money. It’s important to note that the amount of value depends on the type of catalytic converter.
First, you should do a visual inspection of the catalytic converter. If there is any visible damage or blockage near the exhaust pipe, this could indicate that the catalytic converter is clogged.
Next, you can perform a vacuum test to check for back pressure. To do this, you need an adaptor hose and vacuum gauge connected to the exhaust pipe of your vehicle. Then, you should check for any sudden drops in pressure that could indicate a clogged catalytic converter.
Finally, an oxygen sensor test can be performed to measure the amount of oxygen present in the exhaust stream. If there is too little or too much oxygen present, this can indicate a clogged catalytic converter that needs to be replaced.
If any of these tests indicate a clogged catalytic converter, you should consult with an automotive technician for further diagnosis and repair. It is important to address this issue quickly as it could cause damage to your vehicle if left unchecked. By performing these simple tests, you can detect whether or not your catalytic converter is clogged and take the necessary steps to fix the issue.
The answer is yes, depending on the severity of the damage and how long it has been left untreated. When a catalytic converter becomes damaged, however, these gases can no longer be filtered properly, leading to a build-up of toxic gases in the engine. This can cause the engine to malfunction and eventually result in its destruction if not addressed promptly.
Some common causes of a damaged catalytic converter include insufficient fuel combustion (lack of regular tune-ups), overworking the engine, or chemical contamination from other parts of the exhaust system. Additionally, foreign objects can become lodged in the converter and damage it if left unchecked.
